Notes on Theory of Constraints (TOC)
“Theory of Constraints (TOC)” was first introduced by Eliyahu M. Goldratt in his 1984 book titled The Goal. Since then it has been applied to many industries with great success. The basic premise of the theory is that in every system there is one constraint and by identifying and modifying this constraint we can improve system performance. As address one constraint, we will uncover another constraint somewhere else in system and the cycle of continues improvement can keep on till the constraint is moved out of the system.
3 questions
- What to change?
- To what to change to?
- How to cause the change?
Layers
- Layer 1 - achieving agreement on the problem
- Layer 2 - achieving agreement on the direction of the solution
- Layer 3 - achieving agreement on the solution
- Layer 4 - achieving agreement that there are no negative effects
- Layer 5 - achieving agreement that we can overcome implementation obstacles
3 basic assumptions of TOC
- Convergence-reality
- Win-win - no conflict between local and global exists
- Handle people with respect
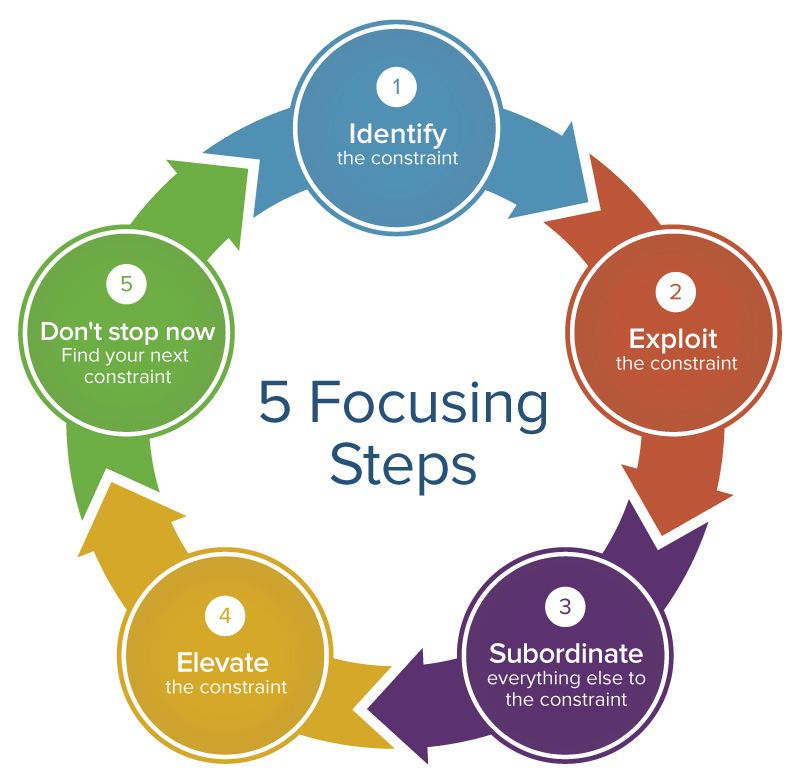
Five Focusing Steps
- Identify
- Exploit
- Subordinate
- Elevate
- Repeat
Types of constraint
- Physical
- Policy
- Paradigm
- Market
Tools
- EC (Evaporating cloud)
- CRT (Current Reality Tree)
- FRT (Future Reality Tree)
- PRT (Pre-requisites Tree)
- TRT (Transition Tree)
The Cloud (EC)
Parts of the cloud
- Objective - A
- Need or necessary conditions - B & C
- Tactics - D & D’
Applications
Inner dilemma
- Who, what, when, where? What did I want to do? Why? What did I feel forced to do? Why?
- D/D’ –> C –> B –> A
- D - the most forced action
- D’ - the most preferred action
Day to day conflicts
- Other side - B <– D
- Your side - C <– D’
- Analyze to prevent in future
Firefighting prevention
- B –> D –> D’ –> C –> A
- Start with B - the need that was jeopardized and triggered the fire
UDE
- B –> D –> C –> D’ –> A
- System UDE & Customer UDE
- UDE’s do not imply a hidden solution
Steps to draw cloud
- Step 1 - identify type of problem
- Step 2 - write a storyline
- Step 3 - build the cloud
- Step 4 - check the logical statements
- Step 5 - surface the assumptions
- Step 6 - construct your solution
- Step 7 - communicate the solution
Syntax Guidelines
- Whole sentences
- No causality
- D & D’ are clear and directly conflict actions
- B & C are clear and positive needs
